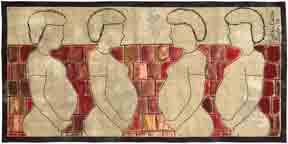
Excitement is building as the start date for my new online class is fast approaching. Introduction to Thread Painting begins April 1. That’s next week and there are still a few spaces available.
Additionally, in the coming months, I will begin Color & Composition courses, and will offer Coaching Sessions, along with free behind the scenes content for all to enjoy.
I feel strongly that connection is essential to successful learning, and hope to build a vibrant, sharing community where creators feel emboldened to learn and apply new skills and concepts. If this appeals to you, read on to find more details about each of my offerings…
Introduction to Thread Painting will begin April 1.
-Course includes 12 lessons that increase in difficulty and complexity to help you build your
-Each lesson includes an instructional video, lesson notes, support materials, and ideas for further exploration.
–Because I believe face-to-face contact is so important to learning: All participants are invited to join a weekly video check-in with Lea on Wednesday evening, or Saturday afternoon.
-A new lesson becomes available each Monday for 12 weeks, with an additional 4 weeks access to all course materials.
-The cost of the course for Beta testers is $180. That is just $15/lesson
To learn more CLICK HERE
Color & Composition courses-Coming soon!

-There is so much information to cover on these topics that it will be divided into 2 courses. Color & Composition I will be available in June 2024, and Color & Composition II be offered in January 2025.
-Each class meets for a 2-hour online video session once a month for 6 months.
-Each session features an in-depth look at a color scheme, a concept related to color, and another related to composition, along with ideas for further creative exploration.
-Participants will respond to monthly challenges and share their work at the next meeting where we will celebrate and give feedback as requested.
-This is meant to be a very nurturing experience that provides inspiration and encouragement, while celebrating experimentation and artistic exploration.
To learn more about this, and other upcoming courses and offerings, CLICK HERE
Individual and Group Coaching Sessions available in the coming months.
-This is an opportunity to talk through iussues or obstacles encountered in
-Advice and guidance is also available related to submitting to competitions and exhibitions, publishing, and teaching about your work.
-Sessions are offered for 30 or 60 minutes via video conferencing.
-These are single session events, so no long tern commitment.
-Sessions are suitable for individuals, or a small group working on a single project.




















 Interested in learning more? Every month I lead a Color and Composition class where we explore a color scheme, color concept, and a composition concept. We meet online the 4th Saturday of every month 1:00-3:00 PM MDT. To join us, sign up through the
Interested in learning more? Every month I lead a Color and Composition class where we explore a color scheme, color concept, and a composition concept. We meet online the 4th Saturday of every month 1:00-3:00 PM MDT. To join us, sign up through the